Power You Can Count On: Paper-Covered Winding Wires for Reliable Transformers
The Vital Role of Insulation Paper-Covered Winding Wires in Transformer Reliability
When it comes to transformer performance, it’s often the unseen components that make the biggest impact. Paper-covered winding wires are one such element, quietly performing critical functions at the heart of every transformer.
Wound tightly around the transformer core, these conductors do more than carry current, they deliver consistent, long-term performance thanks to their expertly engineered insulation. Whether it’s withstanding extreme temperatures or providing the structural integrity needed to endure mechanical stress, paper-covered wires are essential to powering the grid behind the scenes.

Why They Matter
- Robust Insulation
The paper wrap prevents current leakage and electrical faults, enhancing safety and efficiency. - Thermal Resilience
Built to handle the heat, these wires stand up to the high temperatures of active transformer operation. - Design Flexibility
With multiple paper types available, the wires can be tailored to suit a range of configurations and requirements.
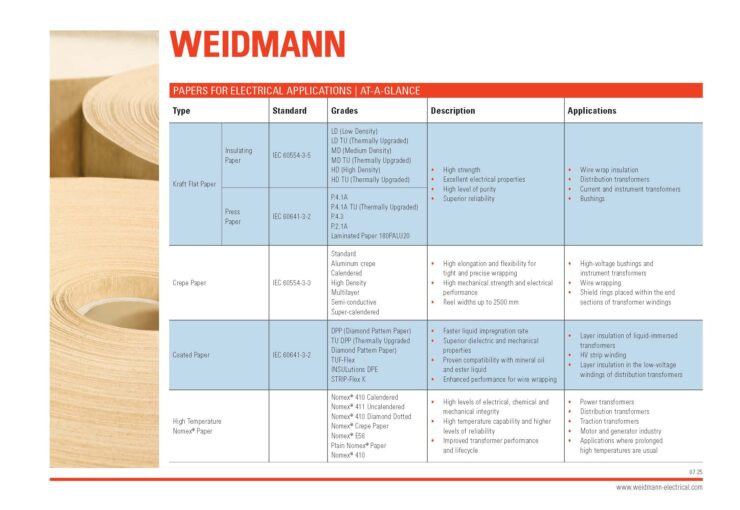
Application of Cellulose Insulating Papers in Transformers and Their Components
- Distribution transformers – including layer winding insulation, main insulation between HV and LV windings and between windings and ground, end strips, duct strips, ladders, and lead insulation e.g. crepe paper tubes.
- Power transformers – including conductor (magnet wire) insulation, lead insulation, and stress (static) ring insulation.
- Components – including bushings and active part insulation
Layer Winding Transformer Papers
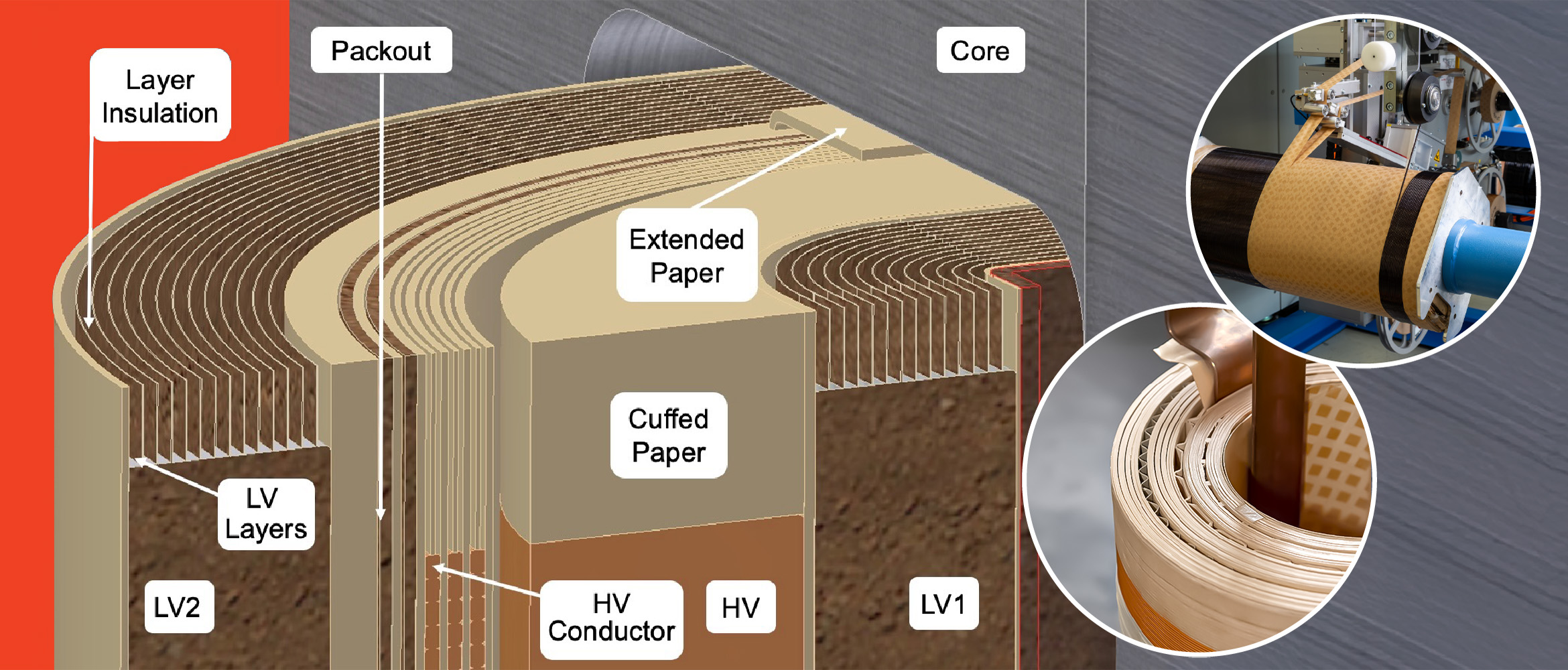
Paper is generally the primary insulation material in liquid-filled transformers whose coils are wound in layers. Conductor materials are wound in layers, and insulation paper is wound between those layers as interlayer insulation. Layer winding transformers are also commonly referred to as “distribution” transformers, although some larger layer winding transformers can be called small power transformers.
The conductor is typically a thin sheet conductor in the Low Voltage (LV) windings of distribution transformer coils, often called “foil”, of either aluminum or copper. In the High Voltage (HV) winding of distribution transformer coils, the conductor is typically a smaller cross-section of aluminum or copper wire, either a round or rectangular is shape. In both LV and HV windings, the layers of conductor materials are insulated with layer insulation paper. In addition to layering insulation, paper is used as the end fill strips in both LV and HV windings, which provide mechanical support to the windings.
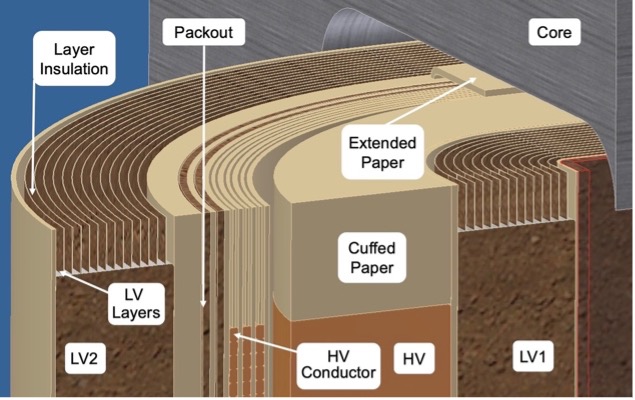
Paper Insulation for LV and HV Windings of Distribution Transformers
Papers suitable for an LV winding of a distribution transformer include uncoated and epoxy resin diamond pattern printed coated presspapers (commonly referred to as DPP), and thermally upgraded presspapers developed to provide increased efficiency, higher temperature resistance, and a smaller physical footprint.
Paper Insulation for Conductor Wires
Kraft flat papers are typically used for conductor wire insulation due to their strength and elongation properties. This paper’s high level of purity provides superior levels of reliability and long-term performance required for wire wrapping machines.
Paper Insulation for Bushings and Instrument Transformers
A variety of crepe papers and some kraft flat papers are used in bushings and instrument transformers.
Choose the Right Paper
From classic kraft paper to high-performance materials like Nomex® and thermally-upgraded paper, the choice of insulation defines performance. Each brings its advantages in terms of strength, heat resistance, and application flexibility.